Kids with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have inflammation (swelling and irritation) of the digestive tract. The inflammation causes belly pain, diarrhea, low energy, weight loss, and other problems. There are two kinds of IBD: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC). IBD is treated with medicines, changes in diet, and sometimes surgery.


Your child:
Your child:

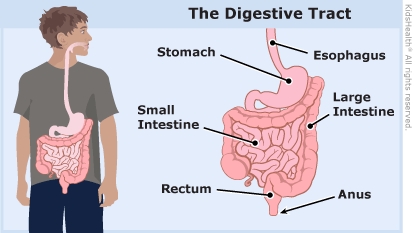
How do Crohn's disease and UC differ? Crohn's disease can happen in the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum, and anus. UC happens only in the large intestine. Crohn's disease has inflammation that goes through the whole wall of the intestine. UC has inflammation only in the inner lining of the large intestine.
What are the signs of IBD? Kids with IBD may have belly pain, diarrhea, blood in the poop, tiredness, weight loss, fever, rashes, and/or joint pain. They may grow slowly or go through puberty later than usual. When IBD gets worse, it is called a flare. Remission is when the signs of IBD are better or gone. Although the signs of IBD come and go, it is a lifelong condition.
What tests are done to diagnose IBD? Doctors can: