Many kids and teens have coughing at times. Usually, it goes away on its own and isn't a sign of a serious illness.
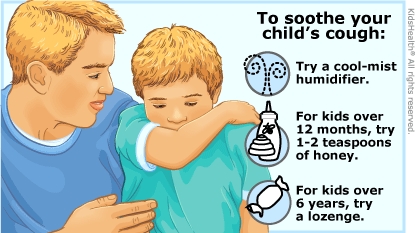
Treatment for a cough depends on the cause. You can do things at home to make your child more comfortable while the cough gets better.
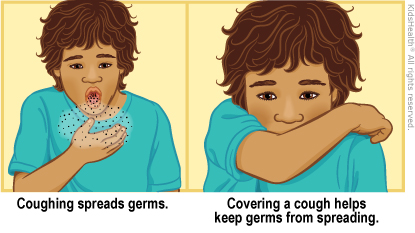


Your child:
Call 911 if your child struggles to breathe, is too out of breath to talk or walk, or turns blue.

Why do kids cough? Coughing is how the body clears the airways in the lungs. Coughs can be caused by:
Can kids go to school if they have a cough? Most kids and teens with a cough can return to school if they haven't had a fever for 24 hours and feel well enough to do regular activities. Ask your health care provider if you're unsure if your child is OK to return to school.
Does a cough always need to be treated? Not always. Only treat a cough if it bothers your child or makes them uncomfortable. If your child feels good, eats and sleeps well, and is playing normally, a cough might not need any treatment.