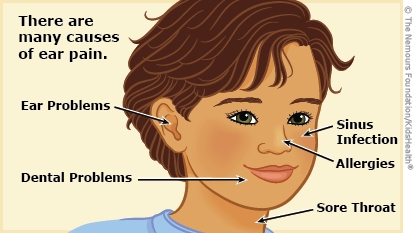
Many things can cause ear pain, including infections, allergies, a cold or a sore throat, fluid behind the eardrum, earwax buildup, a tooth problem, or a sinus infection.
Follow these care instructions to help your child feel better.



Would an antibiotic help my child? No. Antibiotics only work against bacteria, and your child's ear pain doesn't appear to be due to a bacterial infection. Antibiotics can't treat infections caused by viruses (such as a cold, the flu, and many ear infections).
Health care providers prescribe antibiotics only as needed. Antibiotics can have side effects (such as nausea or diarrhea), cause allergic reactions, and lead to other infections (such as yeast infections). Taking antibiotics too often or for the wrong reasons can change bacteria so much that antibiotics don't work against them. This is called antibiotic resistance. The changed bacteria can spread to others and cause serious infections.
How will I know if my child's ear pain is due to an infection? If your child's symptoms get worse, new symptoms happen, or the ear pain doesn't get better within a few days, your health care provider will see your child again and do an exam to check for an ear infection.