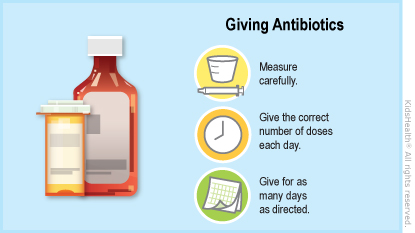
Antibiotics are medicines that treat infections caused by bacteria (types of germs). Your child has an infection caused by bacteria and needs to take an antibiotic to get better. For the antibiotic to work properly, your child needs to take it exactly as prescribed.

Your child should take ALL doses of the antibiotic as prescribed, even if they start to feel better. This is the best way to kill the harmful bacteria.
Follow your health care provider's or pharmacist's instructions on:
- How often to give the antibiotics each day
- How many days your child should take the antibiotics
- How to store the antibiotics (for example, at room temperature or in the refrigerator)
- If your child should take the antibiotics with or without food
- If your child needs to avoid eating any foods while taking the antibiotics
Other reminders:
- Before giving any medicine, always check the label to make sure you're giving the right medicine and that it hasn't expired.
- Use the medicine device (cup or dropper) that comes with the antibiotic.
- If the antibiotic is a pill, tablet, or capsule, don't crush it unless you check with your health care provider or pharmacist first.
- Never give your child medicines prescribed for someone else.
- If your child misses a dose, give the next dose as prescribed and continue giving the antibiotics as directed. Don't give more than one dose at a time. If your child misses more than one dose, call your health care provider.
- While your child is on antibiotics, check with your health care provider or pharmacist before giving your child any other medicines.
- Alcohol can make some antibiotics not work as well. Talk to older kids and teens about the importance of not drinking alcohol, especially while taking any medicines.
- Some antibiotics can make hormonal birth control medicines (like the Pill) not work as well. Talk to your health care provider about whether your child needs a backup method of birth control while taking the antibiotic.
Your child has signs of an allergic reaction, such as:
- Hives (raised red welts on the skin)
- Trouble breathing or swallowing
- Swelling of the throat or tongue
- Vomiting again and again

How do antibiotics work? Antibiotics treat infections by killing bacteria or by stopping bacteria from growing and multiplying. Antibiotics can only treat infections caused by bacteria. They can't treat infections caused by viruses (like colds or the flu).
Why should I keep giving the medicine if my child is starting to feel better? Stopping antibiotics early may not treat the whole infection, and the infection may come back. Also, the infection may be harder to treat in the future. So your child should take all doses of the antibiotic as directed.
What if my child has a hard time swallowing a pill? If your child has trouble swallowing a pill, ask your health care provider if you can crush it and mix it with a small amount of liquid or soft food, such as applesauce. (Some pills should not be crushed.) If your health care provider says it's OK, make sure your child swallows the entire portion to get the complete dose.