Growth hormone deficiency means someone's pituitary gland (a part of the brain) doesn't release enough growth hormone. Kids with the condition are shorter than other kids their age. They may have other problems too. If treatment with growth hormone injections is started early, many kids with growth hormone deficiency can grow to a normal height. Follow these instructions to care for your child.


Your child gets new symptoms such as headaches, hip pain or knee pain, enlarged breasts, or a limp. These can be side effects from treatment with growth hormone.

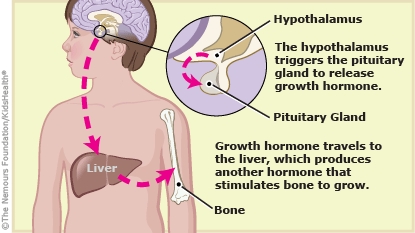
What happens in growth hormone deficiency? Normally, the hypothalamus (a part of the brain just above the pituitary gland) sends messages to the pituitary gland, triggering it to release growth hormone into the blood. Growth hormone then signals the liver to release another hormone that causes bones to grow. In growth hormone deficiency, the pituitary gland doesn't make or release enough growth hormone, so the bones don't grow normally.
What causes growth hormone deficiency? Someone can be:
What other problems can happen if growth hormone deficiency isn't treated? Besides poor growth, people with untreated growth hormone deficiency may have low bone mineral density (weak bones), a higher risk of heart disease, and low energy.