Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection that leads to small flesh-colored bumps that often have a tiny dent in them. It's caused by a virus (a type of germ). The bumps aren't painful but may itch. Molluscum contagiosum usually goes away on its own within 6 to 12 months, but it can last longer. If needed, your health care provider can recommend treatments to help it clear up faster, such as creams or minor procedures.
Molluscum contagiosum can spread through skin-to-skin contact, sharing towels or clothing, or touching the bumps, then touching other parts of the body.
Here's some information to help you care for your child and prevent the spread of molluscum contagiosum.
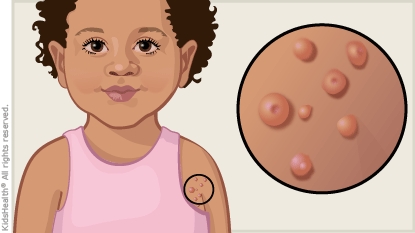

Follow your health care provider's instructions for:
Follow these tips to prevent molluscum contagiosum from spreading:
Other tips:


What problems can happen from molluscum contagiosum? The bumps usually are painless, but if your child scratches or picks at them, they can get infected with bacteria (another type of germ). If that happens, a child may need antibiotic treatment.
What happens if molluscum contagiosum doesn't go away? If the infection doesn't go away or gets worse, your health care provider may treat it by: