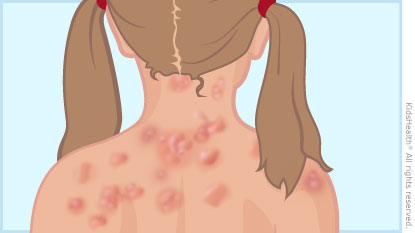
Acute hives are red, itchy bumps or swellings that suddenly appear on the skin. On darker skin, color changes can be harder to see. Hives are often triggered by an allergic reaction, but there can be other causes. Symptoms usually can be relieved by taking antihistamines and avoiding any known triggers.


Your child has signs of a serious allergic reaction, such as:
If your health care provider gave you a prescription for an epinephrine auto-injector, make sure you know how to use it and follow the instructions exactly. If you need to use it, call 911 afterward or go to the ER to see if your child needs further treatment. This is true even if your child is doing better, because there can be a second wave of symptoms. Take the used epinephrine auto-injector with you to the hospital.

Why do acute hives happen? Acute hives, also known as acute urticaria, happen when immune cells in the skin (mast cells) release the chemical histamine. Histamine causes itching, redness, and swelling.
Causes of hives include:
Often the cause of hives is not found.
How are hives treated? In many cases, mild hives go away without treatment. The health care provider may recommend an antihistamine or other medicine to help with the itching. Hives may sometimes come and go over a period of minutes to days.
Are hives contagious? No, hives are not contagious. Even hives caused by an infection can't spread to others.