Kids with Crohn's disease have inflammation (swelling and irritation) of the digestive tract. This inflammation causes belly pain, diarrhea, low energy, weight loss, and other problems. Crohn's is treated with medicines, changes in diet, and sometimes surgery. Follow these instructions to help get your child's symptoms under control.


Your child:
Your child:

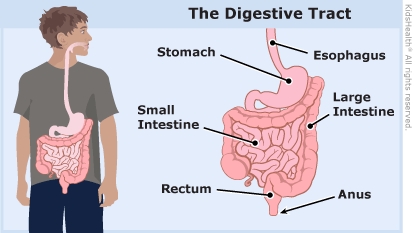
What happens in Crohn's disease? People with Crohn's disease have inflammation and sores in the digestive tract. The digestive tract includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum, and anus. Crohn's usually happens in the intestines.
What are the signs of Crohn's disease? Kids with Crohn's may have belly pain, diarrhea, blood in the poop, tiredness, weight loss, fever, rashes, and/or joint pain. They may go through puberty later than usual and grow slower or be shorter than other kids their age. When Crohn's disease gets worse, it's called a flare (or flare-up). Remission is when the signs of Crohn's disease get better. The symptoms of Crohn's come and go, but it is a lifelong condition.
Why do kids get Crohn's disease? The cause of Crohn's disease isn't clear, but it's probably a combination of:
What tests are done to diagnose Crohn's disease? To diagnose Crohn's disease, health care providers: