Hypoglycemia is when the body has low blood sugar. It can happen if someone takes certain medicines, doesn't eat for a long time, drinks alcohol, takes medicines that aren't meant for them, or has a medical condition. How hypoglycemia (hi-po-gly-SEE-me-uh) is treated depends on what caused it.
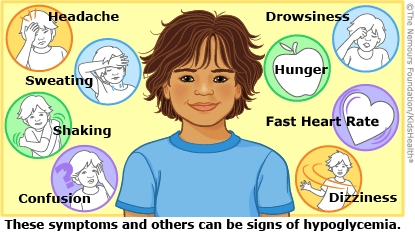
Your child had an episode of hypoglycemia. They may have had shaking, hunger, sweating, or other symptoms. Their blood sugar is now back to normal, and they can be cared for at home.

Follow your health care provider's instructions for:
If your child has symptoms of hypoglycemia again:


Why is it important to treat hypoglycemia? Untreated hypoglycemia can lead to passing out, seizures, and even a coma. It also can slow a child's brain development.
What does glucose do? Glucose, a type of sugar, is the body's most important source of energy. The body needs a certain amount of glucose to function. If the level isn't right, it causes symptoms.