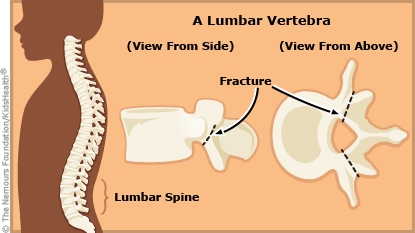
Spondylolysis (spon-duh-LOL-uh-sis or spon-duh-low-LIE-sis) is a fracture (crack or break) in a bone in the spine called a vertebra. It can happen from repeated stress or from an injury to the spine. It usually heals quickly with rest and physical therapy.


Your child:
Your child:

How does a back stress fracture happen? A back stress fracture can develop over time as a child's growing spine is put under repeated stress from lots of bending, twisting or tightening of the back muscles.
Young people have a greater chance of getting spondylolysis because their bones are still growing. Kids and teens who do sports and activities that can strain the lower back or that involve a lot of leaning back are especially likely to develop it. This can include football, weightlifting, gymnastics, volleyball, ballet, golf and wrestling.
When can my child return to sports and activities? Most kids and teens with a back stress fracture will feel better in 3 months. Your child should wait until the pain is gone and there are no problems when moving before playing contact sports or doing challenging activities. To help prevent more serious back problems, an injury should be completely better before your child returns to these activities.
What can we do to prevent more problems in the future? After recovery, kids and teens need to keep up with the proper techniques and sports safety measures they learned. They should keep their core muscles strong and flexible, and take breaks between sports seasons, games and competitions. Kids and teens should immediately stop doing any activity that causes back pain. They should see their health care provider and not return to play until the pain goes away.