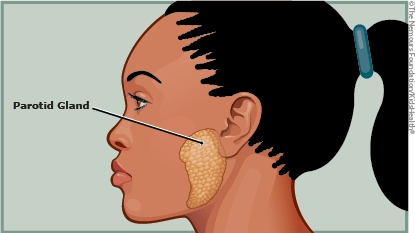
Mumps is caused by the mumps virus. It was a common childhood infection, but now is rarer thanks to the mumps vaccine. Kids with mumps usually have painful swelling of the parotid glands. These glands, which make saliva (spit), are in front of the ear, around the jaw. They also might have a fever, headache, muscle aches, tiredness, and loss of appetite. Most children with mumps recover fully in about 2 weeks with basic home care.


Your child:
Your child:

How does mumps spread? The mumps virus spreads in tiny drops of fluid when someone sneezes, coughs, talks, or laughs. It also can spread by sharing objects used by an infected person, such as utensils, or touching contaminated objects or surfaces. It is most contagious a few days right before and 5 days after parotid gland swelling.
How do health care providers treat mumps? There's no specific medical treatment for mumps. Home care focuses on managing symptoms. Because mumps is caused by a virus, antibiotics can't treat the infection. Antibiotics are effective only against bacteria.
Can mumps be prevented? Yes, the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine can prevent mumps. Be sure that all family members get their recommended vaccines on time. It's especially important for college students and people living in close quarters to get both doses of the vaccine. During a mumps outbreak, some people sometimes need a third dose. Your health care provider will have the most current information.