Hoarseness is when a person's voice sounds rough, raspy, weak, or breathy. It happens when the vocal cords get irritated or strained. In kids, hoarseness is usually caused by a viral infection or by straining the voice through yelling. Resting the voice helps hoarseness get better.


Your child:
Your child's hoarseness suddenly becomes severe and makes it hard for your child to breathe.

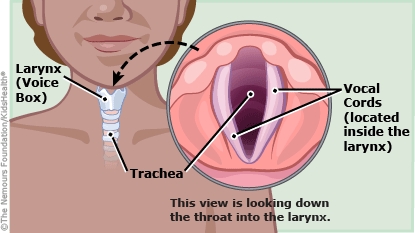
What are the vocal cords? The vocal cords are delicate bands of tissue in the larynx (LAIR-inks), or voice box. When we speak, air pushes out of the lungs and passes through the vocal cords, causing them to vibrate. This vibration, combined with the movement of the tongue, lips, and teeth, is what makes the sound of the voice.
Why does hoarseness happen? Hoarseness happens when something irritates the vocal cords, such as:
Rarely, hoarseness can have a more serious cause.
What happens if the hoarseness doesn't go away? Hoarseness that lasts more than 2 weeks is called "chronic hoarseness." If that happens, your health care provider may refer your child to an otolaryngologist (an "ear, nose, and throat" [ENT] doctor) and a speech pathologist. These specialists can do tests to find out what is causing the hoarseness and make a treatment plan to help your child.