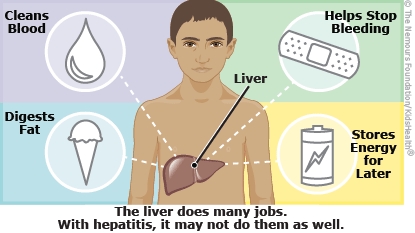
Hepatitis C is when the liver is infected by the hepatitis C virus and might not work as well as it should. The liver, an organ in the right upper abdomen, has several jobs, including breaking down fatty food, storing energy, clearing toxins from the blood, and making proteins that help blood to clot.
Hepatitis C often does not cause symptoms. When it does, it may cause fever, feeling tired, belly pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), joint pain, and nausea or vomiting. While kids may feel fine within a few weeks, the infection often remains, and they may need to see a liver specialist.
People with hepatitis C can be treated with medicine to help avoid problems in the future. Medicine often cures the infection.


Your child:
Your child:

How do people get hepatitis C? Hepatitis C can spread through sexual contact, sharing contaminated needles or other items (like razors or toothbrushes), or kidney dialysis. A mother with hepatitis C can pass it to her baby during childbirth. Some people have few or no symptoms. Even without symptoms, an infected person can pass the hepatitis C virus to others.
What can protect others from getting hepatitis C? To prevent the spread of hepatitis C, people should always use condoms when having sex, not use intravenous drugs or share needles, and not share toothbrushes or razors. Someone with hepatitis C should not donate blood.