Breast milk gives babies the nutrition they need and offers health benefits for both mother and child. Babies who are breastfed are less likely to get infections, allergies, and some illnesses. Many of these benefits last well into childhood.
Breastfeeding is natural, but it can take practice for you and your baby to feel comfortable. Here are some tips that can help.
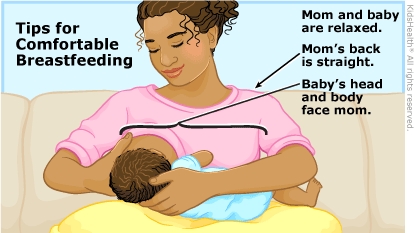

Take Care of Yourself
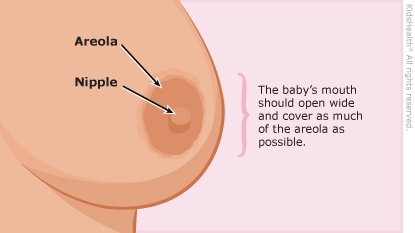

Your baby:
You:

I am finding breastfeeding hard. Where can I get help? Breastfeeding takes time and practice. If you feel down or sad, or if you have trouble taking care of your baby, talk to your health care provider about getting help. A lactation consultant or mother's support group also can offer help and support with breastfeeding.
You can get help online at: