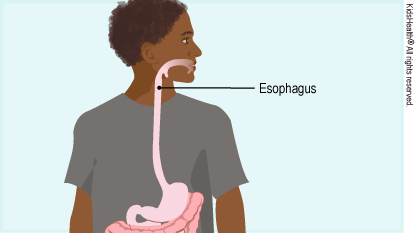
People with eosinophilic esophagitis have a buildup of a type of allergy cells called eosinophils (ee-eh-SIN-eh-fils) in their esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach). This buildup leads to inflammation (irritation and swelling) in the esophagus, which can cause trouble with eating and swallowing, chest pain, heartburn, belly pain, and vomiting.
Symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis (ee-eh-sin-eh-FIL-ik eh-sof-eh-JYE-tis) often improve with treatment.


Your child:

What causes eosinophilic esophagitis? It's not always clear why eosinophilic esophagitis happens. Some people develop it due to an allergic reaction to foods or something in the environment. But it also can happen in someone with no history of allergies. It's more common in people who have other allergy-related conditions, such as food allergies, asthma, and eczema.
What long-term problems can happen? In some people, eosinophilic esophagitis can lead to: